Head-on collisions are among the deadliest accidents on the road. Learning how to avoid them can save lives—including yours.
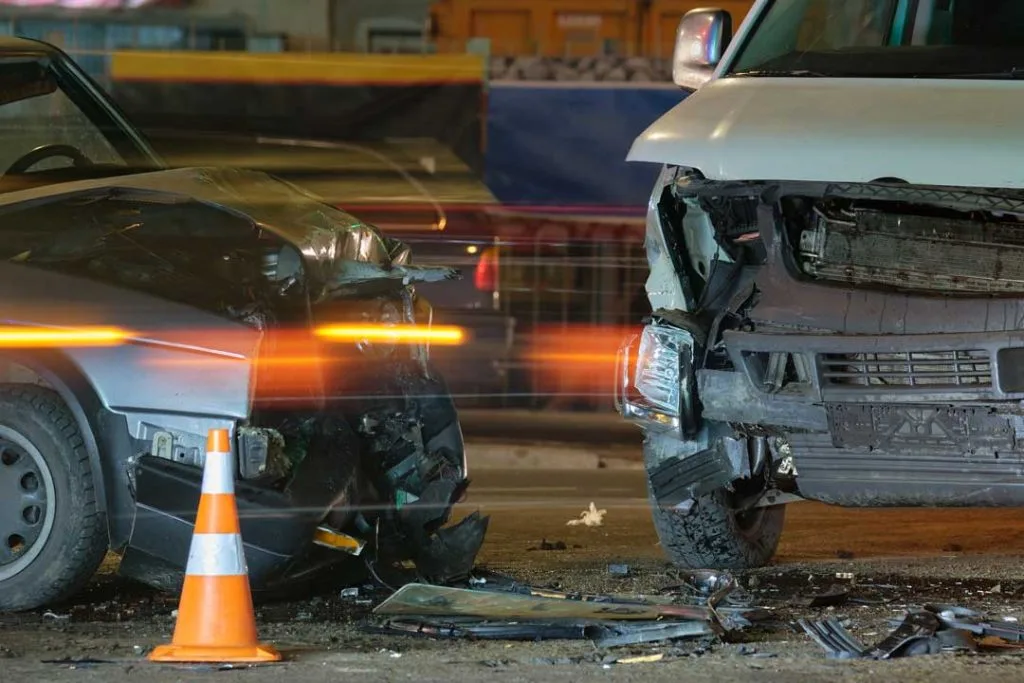

Head-on collisions are among the most devastating types of traffic accidents. Despite accounting for only a small percentage of all crashes, head-on collisions are responsible for a disproportionately high number of fatalities.
The combined impact forces of two vehicles traveling in opposite directions create catastrophic results, often leaving drivers and passengers with severe injuries or worse. Understanding how to avoid these collisions is essential for every driver. This comprehensive guide explores the causes of head-on crashes and provides practical strategies to prevent them.
Understanding Head-On Collisions
A head-on collision occurs when two vehicles traveling in opposite directions crash into each other front-to-front. These accidents typically happen on two-lane roads, rural highways, or when a vehicle crosses the centerline or median into oncoming traffic.
The physics of these crashes is particularly brutal: the impact force equals the combined speed of both vehicles. A collision between two cars each traveling at 45 mph creates an impact comparable to hitting a solid wall at 90 mph.
Common Causes of Head-On Collisions
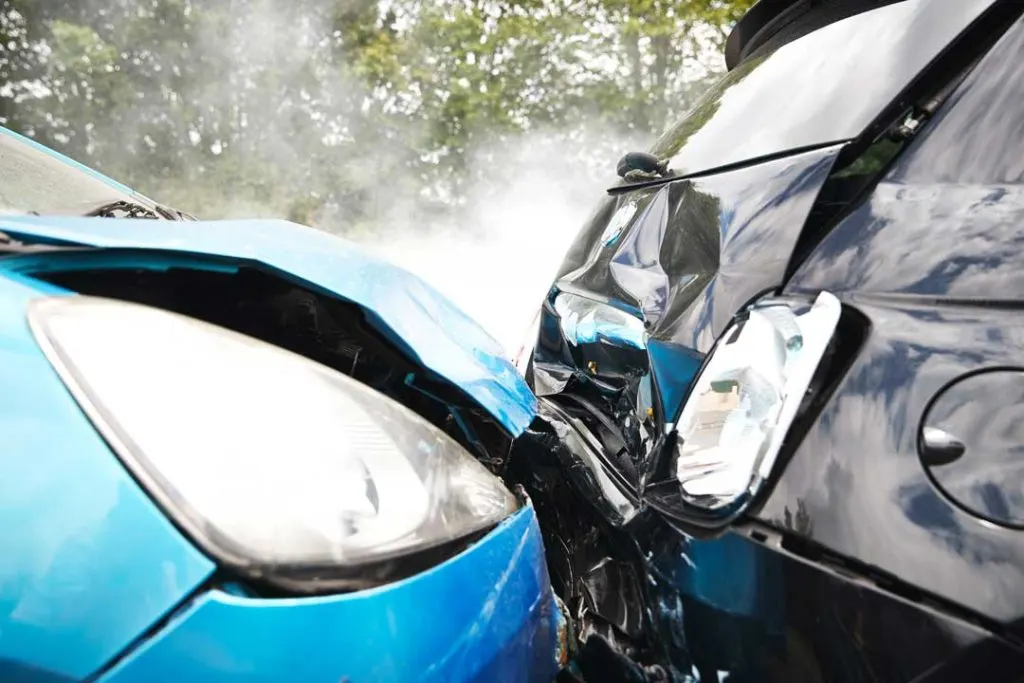

Understanding the primary causes of these accidents is the first step toward prevention:
Distracted Driving: Taking your eyes off the road for even a few seconds to check a text message, adjust the radio, or attend to children in the backseat can lead to lane departure and potential head-on collisions.
Impaired Driving: Alcohol and drugs significantly impair judgment, reaction time, and coordination. Impaired drivers often drift across centerlines or drive in the wrong direction.
Fatigue: Drowsy driving can be as dangerous as drunk driving. Microsleeps—brief, involuntary periods of unconsciousness lasting seconds—are particularly hazardous, as a vehicle can travel hundreds of feet during this time.
Unsafe Overtaking: Attempting to pass slower vehicles without adequate visibility or sufficient passing zones is a leading cause of head-on crashes on two-lane roads.
Poor Weather Conditions: Rain, snow, fog, and ice reduce visibility and traction, increasing the likelihood of a vehicle crossing into oncoming traffic.
Unfamiliar Roads: Navigating unfamiliar areas, especially at night or in poor weather, can lead to wrong-way driving or missed turns.
Mechanical Failures: Tire blowouts, steering system failures, or brake malfunctions can cause sudden loss of control.
Preventive Strategies

Avoiding head-on collisions requires a proactive approach to driving. By staying alert, making smart passing decisions, adapting to environmental conditions, and keeping your vehicle in top shape, you can reduce risks on the road.
Defensive driving techniques, combined with responsible vehicle maintenance, help ensure you stay in control and prepared for unexpected situations. The following strategies will equip you with the knowledge to drive safely and confidently in any situation.
Defensive Driving Techniques
Stay Alert and Focused: Eliminate distractions by putting away electronic devices, pre-setting your navigation system, and adjusting controls before driving. If you need to make adjustments while driving, find a safe place to pull over.
Maintain Lane Position: Keep your vehicle centered in your lane, especially on narrow roads. Pay attention to lane markings and road edges.
Scan the Road Ahead: Look far ahead while driving to spot potential hazards early. This practice, known as “high visual horizon” driving, gives you more time to react to oncoming vehicles that might cross into your lane.
Adopt the “What If” Mindset: Anticipate potential hazards and mentally rehearse escape routes. Ask yourself: “What if that oncoming car crosses the centerline?” or “What if that truck’s load falls off?”
Leave Space for Evasive Action: Maintain adequate following distance from vehicles ahead to provide maneuvering room in emergencies.
Safe Overtaking Practices
Verify It’s Legal: Only pass where permitted by road signs and markings.
Ensure Clear Visibility: Make sure you can see far enough ahead to complete the pass safely. Hills, curves, and weather conditions can reduce visibility.
Check for Sufficient Space: Confirm you have enough room to pass and return to your lane without forcing an oncoming vehicle to brake or swerve.
Use Turn Signals: Signal your intentions clearly to alert both the vehicle you’re passing and oncoming traffic.
Abort If Uncertain: If conditions change during a passing maneuver, abandon the attempt and return to your lane safely.
Environmental Adaptations
Adjust for Weather: Reduce speed in adverse conditions like rain, fog, or snow. Poor visibility and reduced traction demand extra caution.
Navigate Night Driving Carefully: Darkness significantly reduces visibility. Use high beams when appropriate but switch to low beams when approaching oncoming traffic to avoid blinding other drivers.
Be Cautious on Unfamiliar Roads: Use navigation aids but don’t rely solely on them. Pay close attention to road signs, especially those indicating one-way streets or divided highways.
Mind Rural Roads: Two-lane country roads without median barriers present higher risks for head-on collisions. Be particularly vigilant on these thoroughfares.
Vehicle Maintenance for Prevention
Regular Tire Inspections: Check tire pressure and tread depth routinely. Properly maintained tires provide better traction and handling.
Brake System Checks: Ensure your braking system responds quickly and effectively. Have it inspected during routine maintenance.
Steering System Maintenance: A properly functioning steering system allows for precise control and quick evasive maneuvers when needed.
Lighting: Maintain functional headlights, taillights, and turn signals to make your vehicle visible to others and to illuminate potential hazards.
Emergency Response Strategies
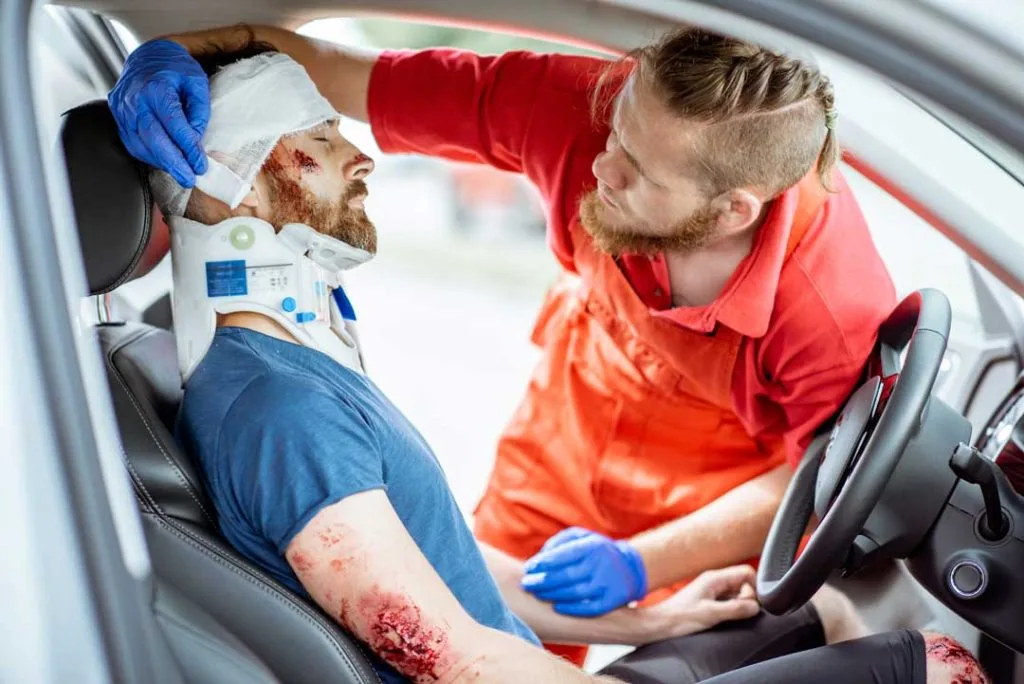

Despite preventive measures, you might still encounter situations where a head-on collision seems imminent. Knowing how to react could save lives:
The “Right-Side” Rule: If an oncoming vehicle crosses into your lane, your instinct might be to swerve left. However, experts recommend steering to the right (toward the shoulder or off-road area). The oncoming driver may realize their error and return to their proper lane at the last moment—if you’ve moved left, you might collide with them as they correct course.
Controlled Braking: Apply brakes firmly but without locking the wheels (if your vehicle lacks anti-lock brakes). This reduces your speed while maintaining steering control.
Horn Usage: Use your horn to alert a distracted or drowsy driver who appears to be drifting into your lane.
Avoid Overcorrection: If you find yourself drifting toward the centerline, don’t jerk the steering wheel. Make a controlled, smooth correction to return to your lane.
Technological Aids

Modern vehicles offer sophisticated safety features designed to prevent head-on collisions:
Lane Departure Warning Systems: These alert drivers when they begin to drift out of their lane without signaling.
Lane Keeping Assist: Beyond warnings, these systems actively help steer the vehicle back into its lane.
Forward Collision Warning: These systems detect potential frontal collisions and warn the driver.
Automatic Emergency Braking: This technology applies the brakes automatically if the driver fails to respond to a collision warning.
Head-Up Displays: By projecting important information onto the windshield, these systems allow drivers to monitor speed and navigation without taking their eyes off the road.
Prevent Head-On Collisions with These Life-Saving Defensive Driving Tips
Head-on collisions may be among the most deadly traffic accidents, but they’re also among the most preventable. By staying alert, practicing defensive driving techniques, maintaining your vehicle properly, and leveraging modern safety technologies, you significantly reduce your risk.
Remember that safe driving isn’t just about protecting yourself—it’s about ensuring everyone on the road returns home safely. The few extra seconds it takes to drive cautiously could save a lifetime of regret.
Jessi is the creative mind behind The Coffee Mom, a popular blog that combines parenting advice, travel tips, and a love for all things Disney. As a trusted Disney influencer and passionate storyteller, Jessi’s authentic insights and relatable content resonate with readers worldwide.
