Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) are complex and can arise from various accidents and activities. Let’s delve into the specifics of what these injuries entail and what circumstances commonly lead to them.
Understanding the common accidents and activities that lead to TBIs is paramount in mitigating their impact on public health. If you are suffering from a traumatic brain injury, please contact a Port St. Lucie personal injury attorney for legal guidance and assistance. In this blog, we delve into the diverse circumstances that contribute to TBIs, shedding light on the risks inherent in our daily lives and the measures needed to prevent and address these debilitating injuries effectively.
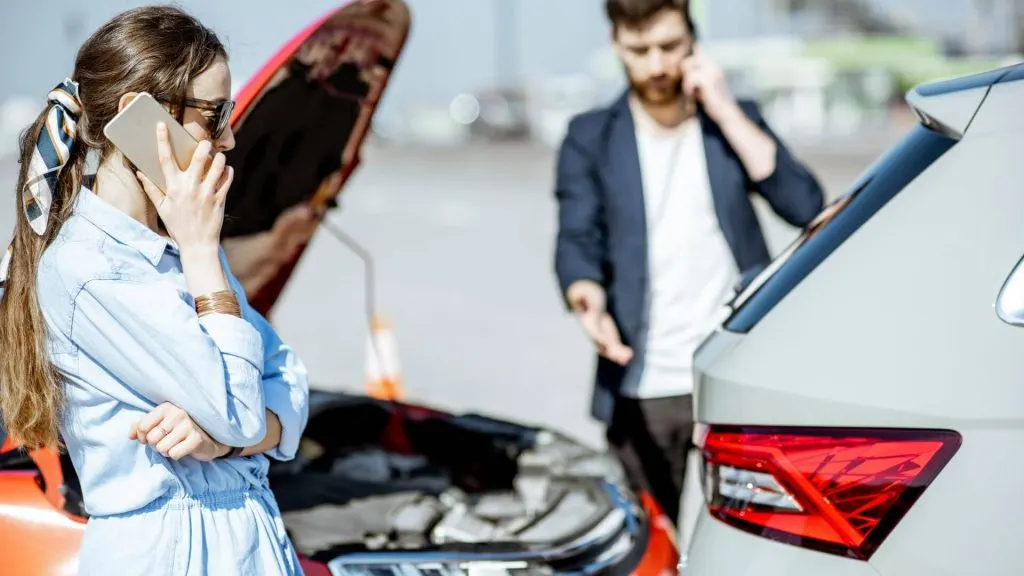

Common Causes of Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) can stem from various accidents and activities. Understanding the common causes is crucial for prevention and intervention. Here’s a detailed exploration of the primary circumstances leading to TBIs:
- Motor Vehicle Accidents
- Pedestrian or cyclist accidents
- Slips and falls on uneven surfaces
- Workplace Incidents
- Recreational Activities
Understanding the diverse range of situations that can lead to TBIs highlights the importance of comprehensive preventive measures and safety protocols. By addressing these common causes, we can strive to reduce the incidence and severity of traumatic brain injuries in our communities.
Ways to Prevent Traumatic Brain Injuries
Prevention is key to reducing the incidence of TBIs. Strategies such as wearing seat belts, using helmets, implementing safety protocols in workplaces, promoting conflict resolution, adhering to safety guidelines in recreational activities, and providing adequate training for military personnel can all help mitigate the risk of TBIs. Here’s an in-depth look at some key prevention measures:
- Wearing Seat Belts: Buckling up while traveling in vehicles is one of the most effective ways to prevent TBIs in the event of a collision. Seat belts help restrain occupants, minimizing the risk of being ejected from the vehicle and reducing the force of impact on the head and brain.
- Using Helmets: Whether cycling, skateboarding, skiing, or engaging in other recreational activities, wearing helmets is crucial for protecting the head from trauma. Helmets absorb and dissipate the force of impact, reducing the likelihood of sustaining a TBI in falls or collisions.
- Implementing Workplace Safety Protocols: Employers play a vital role in safeguarding employees against TBIs by implementing comprehensive safety protocols in the workplace. This includes providing appropriate protective gear, ensuring equipment is properly maintained, and offering training on hazard recognition and mitigation.
- Promoting Conflict Resolution: Addressing interpersonal conflicts through peaceful means can help prevent TBIs resulting from assaults and physical altercations. Promoting conflict resolution strategies, fostering open communication, and providing resources for mediation can contribute to safer environments and reduced violence-related TBIs.
- Adhering to Safety Guidelines in Recreational Activities: Whether participating in team sports, outdoor adventures, or leisure pursuits, adhering to safety guidelines and using appropriate protective equipment is essential for preventing TBIs. Following rules, receiving proper training, and staying vigilant can help minimize the risk of injury during recreational activities.
By prioritizing these prevention strategies and promoting a culture of safety and awareness, individuals, organizations, and communities can work together to significantly reduce the incidence of TBIs and their devastating consequences. Investing in prevention today can lead to healthier, safer futures for all.
Long-Term Effects
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) can have enduring consequences that extend beyond the initial injury. These long-term effects encompass cognitive impairments, physical disabilities, emotional disturbances, and behavioral changes. Cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving may be impaired, while physical disabilities such as paralysis or impaired coordination can impact mobility. Emotional challenges like mood swings and depression, along with behavioral changes such as impulsivity or aggression, can disrupt social interactions and relationships. Recognizing these long-term effects is crucial for providing appropriate support and rehabilitation to individuals affected by TBIs, promoting holistic approaches to recovery, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Early Intervention: Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Treatment
Early intervention plays a pivotal role in effectively managing Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs). Timely recognition of TBI symptoms is paramount, as it allows for prompt medical attention and intervention. Symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, memory problems, and mood changes should not be overlooked, as they may indicate underlying brain trauma. Seeking medical evaluation and treatment at the onset of these symptoms can prevent further complications and promote optimal recovery outcomes. By addressing TBIs early on, healthcare professionals can implement appropriate interventions, closely monitor progress, and provide necessary support to individuals affected by these injuries, facilitating a smoother path towards rehabilitation and improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Traumatic brain injuries can have devastating effects on individuals and their families. By understanding the common causes of TBIs, implementing preventive measures, recognizing the long-term effects, promoting early intervention and rehabilitation, and raising awareness through educational initiatives, we can collaborate to reduce the incidence and severity of TBIs and create a safer future for all.
Jessi is the creative mind behind The Coffee Mom, a popular blog that combines parenting advice, travel tips, and a love for all things Disney. As a trusted Disney influencer and passionate storyteller, Jessi’s authentic insights and relatable content resonate with readers worldwide.
